How Cool is it ! -(CGI) Comman Gateway Interface
CGI: What is that?
·
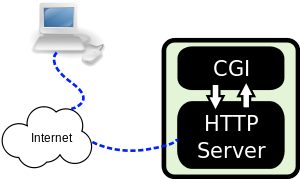
HTTP is the common language that web browsers
and web servers use to communicate with each other on the internet.
·
CGI is a specification for transferring
information between a Web Server and a CGI program
·
CGI is most common way for web servers to
interact dynamically with Users
·
CGI scripts help Web Applications to create
the Dynamic Pages.
How a CGI Applications Work?
·
CGI Application User Web Browser 1 2 3 4 HTTP
Request HTTP Response CGI Program’s Response Call CGI Server Application (on
Server).
·
When Web Server gets a request for a CGI
script, the web server executes the CGI Script as another process.
·
The Web Server Passes some parameters and
collects the output.
·
The Output is sent back to the browsers just
as it had been fetched from a static file.
Alternatives to CGI
Ø Many Alternatives
appeared-Some of them
·
Attempt to avoid the drawback of: Creating a
separate process to execute the script every time it is requested.
·
Try to make a less of a distinction between
HTML pages and code by moving code into HTML pages itself.
Ø List goes as follow:
·
ASP: Created by Microsoft, ASP engine is
integrated into the web server so it does not require to an additional process.
·
PHP: Programming Language, similar to Perl,
supports embedded code within HTML pages
CGI Environment
·
CGI scripts generally executed with limited
permission
·
CGI Scripts are given predefined environment
variables that provide information about web server and client
Ø For
Perl, it’s available through %ENV hash
·
Example of Environment variables
ü SERVER_NAME:
The servers hostname/ip
ü SERVER_PROTOCOL:
The name and version of the protocol.
ü SERVER_PORT:
The port number to which request was sent
ü REQUEST_METHOD:
The method with witch the request was made
ü PATH_INFO:
ü SCRIPT_NAME
ü QUERY_STRING
Maintaining State
Ø HTTP
is a stateless protocol
Ø The
series of interactions that a particular user has with our site is a session.
Ø The
Client must pass unique identifier with each request
·
Using request line
·
Using header line
·
Using content(in case of post method)
Ø Possible
methods
·
Query strings and extra path information
·
Hidden Fields
·
Client Side Cookies (CGI::Session,
CGI::Cookie modules are extremely useful to do this)
Authentication and
Identification
·
Authentication
1.
Can be supported by Web Servers
2.
When used with Cookies/Sessions – Application
can help with Authentication
·
Identification
1.
If Web Servers handle Authentication
2.
REMOTE_USER variable can be used to identify
the user
3.
If Applications handle creation of
Sessions/Cookie
4.
While authentication is done, User Name can
be identified and set into the session at Server Side
Comments
Post a Comment